Building a weighted KNN model to predict house prices using python.
Github link for the project and the data: https://github.com/MNoorFawi/weighted-knn-in-python
Import important libraries.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.neighbors import KDTree from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler import seaborn as sns import random
Import data, remove “id” and “date” columns -unnecessary- and make price a separate variable.
data = pd.read_csv("home_data-train.txt", sep = ",", header = None)
del data[0]
del data[1]
test = pd.read_excel("HomePrices-Test.xlsx", header = 0)
del test["id"]
del test ["date"]
data.columns = test.columns
train_price = data.price
del data["price"]
test_price = test.price
del test["price"]
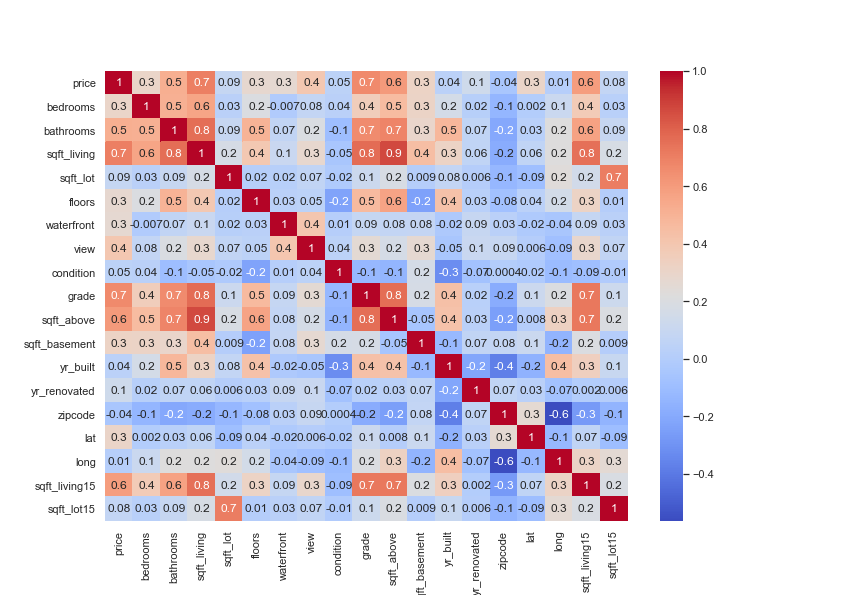
See correlations between each variable and price to extract important variables.
sns.set(rc = {'figure.figsize' : (11.7, 8.27)})
corr = pd.concat([train_price, data], axis = 1).corr()
corr_map = sns.heatmap(corr, annot = True,
fmt = ".1g", cmap = "coolwarm")
Extract important variables and standardize train and test data.
correlated = data.columns[corr.iloc[1:, 0] >= 0.3] scaled = StandardScaler().fit(data[correlated]) train_scaled = scaled.transform(data[correlated]) test_scaled = scaled.transform(test[correlated])
Construct the KDTree and test it.
tree = KDTree(train_scaled)
nearest_dist, nearest_ind = tree.query(test_scaled[13].reshape(1, -1), k = 3)
print(test.loc[13, correlated], "\n")
print(data.loc[nearest_ind[0], correlated], "\n")
print("test price: ", test_price[13], "\n")
print("train price: \n", list(train_price[nearest_ind[0]]))
# bedrooms 2.0000
# bathrooms 2.5000
# sqft_living 1278.0000
# view 0.0000
# grade 7.0000
# sqft_above 1002.0000
# sqft_basement 276.0000
# lat 47.5532
# sqft_living15 1220.0000
# Name: 13, dtype: float64
#
# bedrooms bathrooms sqft_living view grade sqft_above \
# 19933 2 2.5 1233 0 7 963
# 9192 2 2.5 1250 0 7 1030
# 18439 2 2.5 1230 0 7 1060
#
# sqft_basement lat sqft_living15
# 19933 270 47.5533 1230
# 9192 220 47.5243 1250
# 18439 170 47.6007 1290
#
# test price: 358000
#
# train price:
# [360000, 267100, 380000]
Define the weight function, Gaussian, Subtract Weight and the one we will use Inverse Weight, the Weighted KNN algorithm and the Test Algorithm (RMSE) function.
def inverseweight(dist, num = 1.0, const = 0.1):
return num / (dist + const)
def gaussian(dist, sigma = 10.0):
return math.e ** (- dist ** 2 / ( 2 * sigma ** 2))
def subtractweight(dist, const = 2.0):
if dist > const:
return 0.001
else:
return const - dist
def weighted_knn(kdtree, test_point, target, k = 25,
weight_fun = inverseweight):
nearest_dist, nearest_ind = kdtree.query(test_point, k = k)
avg = 0.0
totalweight = 0.0
for i in range(k):
dist = nearest_dist[0][i]
idx = nearest_ind[0][i]
weight = weight_fun(dist)
avg += weight * target[idx]
totalweight += weight
avg = round(avg / totalweight)
return avg
def testalgorithm(algo, kdtree, testset, target, test_target):
error = 0.0
for row in range(len(testset)):
guess = algo(kdtree, testset[row].reshape(1, -1), target)
error += (test_target[row] - guess) ** 2
return round(np.sqrt(error / len(testset)))
Test the algorithm.
random.seed(1191)
ex = random.sample(range(len(test)), 5)
print("predicted",";", "actual", " ;", "error")
for i in ex:
res = weighted_knn(tree, test_scaled[i].reshape(1, -1), train_price)
print(res,
" ;",
test_price[i],
" ;",
abs(test_price[i] - res))
# predicted ; actual ; error
# 446422.0 ; 399995 ; 46427.0
# 542199.0 ; 653500 ; 111301.0
# 331369.0 ; 360000 ; 28631.0
# 375849.0 ; 255000 ; 120849.0
# 633987.0 ; 687015 ; 53028.0
Algorithm’s RMSE.
print(testalgorithm(weighted_knn, tree, test_scaled, train_price, test_price)) #192420.0

Leave a Reply